Sometimes while I am teaching a new math concept, my students look at me like I am speaking in a foreign language. When I teach adding mixed numbers is definitely one of those times! It takes perseverance, for sure, but if speaking in one language usually a second one will. That’s why I’m sharing, not one, but two strategies for how to teach adding mixed numbers. Let’s dive into the step-by-step guide for both of these strategies.
Strategy 1: Teach Adding Mixed Numbers by Breaking Them Apart
One way to teach adding mixed numbers is to show students how to break the mixed numbers apart before adding them. To do this, you can create an anchor chart that outlines the steps needed to solve these math problems. Here are the steps that you can follow to teach adding mixed numbers with this strategy:

Step 1: Add the whole numbers together.
Step 2: Add the fractions together.
Step 3: Simplify the fractional part of the mixed number if necessary.
Step 4: Add to make the mixed number sum.
To teach adding mixed numbers with this strategy, you can use an example mixed number like 3 1/2 + 2 3/4. First, add the whole numbers together (3 + 2 = 5). Next, add the fractions together (1/2 + 3/4 = 5/4). Since 5/4 is an improper fraction, it needs to be simplified. To do this, you can make one whole (4/4) and add it to the mixed number. This will give you a new mixed number of 6 1/4. By modeling this process and practicing with more examples, students can develop a stronger understanding of how to break mixed numbers apart to add them together.
After you’re amazing lesson on breaking apart mixed number to add them, give students plenty of practice. This adding mixed numbers lesson has plenty of fun practice! It includes peer practice activities, an interactive notebook entry, a partner game, and a traditional worksheet–all focused on the break apart to add mixed numbers strategy.
Strategy 2: Teach Adding Mixed Numbers with Improper Fractions
Another approach to teach adding mixed numbers is to show students how to convert mixed numbers into improper fractions. This strategy can be introduced by modeling it a few times and adding it to the anchor chart. Here are the steps to converting mixed numbers into improper fractions:
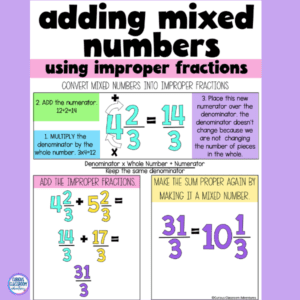
Step 1: Multiply the denominator by the whole number.
Step 2: Add the numerator to the product from step 1.
Step 3: Keep the original denominator.
To teach adding mixed numbers with this strategy, you can use an example mixed number like 2 1/3. First, multiply the denominator (3) by the whole number (2) to get 6. Then, add the numerator (1) to the product from step 1 (6 + 1 = 7). Finally, keep the original denominator (3). This will give you an improper fraction of 7/3. You can repeat this process for another mixed number such as 1 2/5. This will give you an improper fraction of 7/5. Then, teach students how to add two improper fractions and convert the sum into a mixed number. Practicing this with more examples can help solidify the concept in their minds.
Don’t forget to offer tons of practice for this strategy too! This strategy might take a little longer to sink in if your students aren’t already familiar with converting mixed numbers into improper fractions. That’s why playing with the strategy as part of the practice is so great. This adding mixed numbers lesson has all the same great components–lesson, anchor chart, peer practice, game, notebook, plus paper and pencil practice!
By giving students two strategies for adding mixed numbers, hopefully they will find one that fits them just right and find themselves mastering the skill in no time!
P.S. If you are incorporating math games into your lessons you definitely find these math game expectations posters helpful in keeping your gamers on task and behaving appropriately!